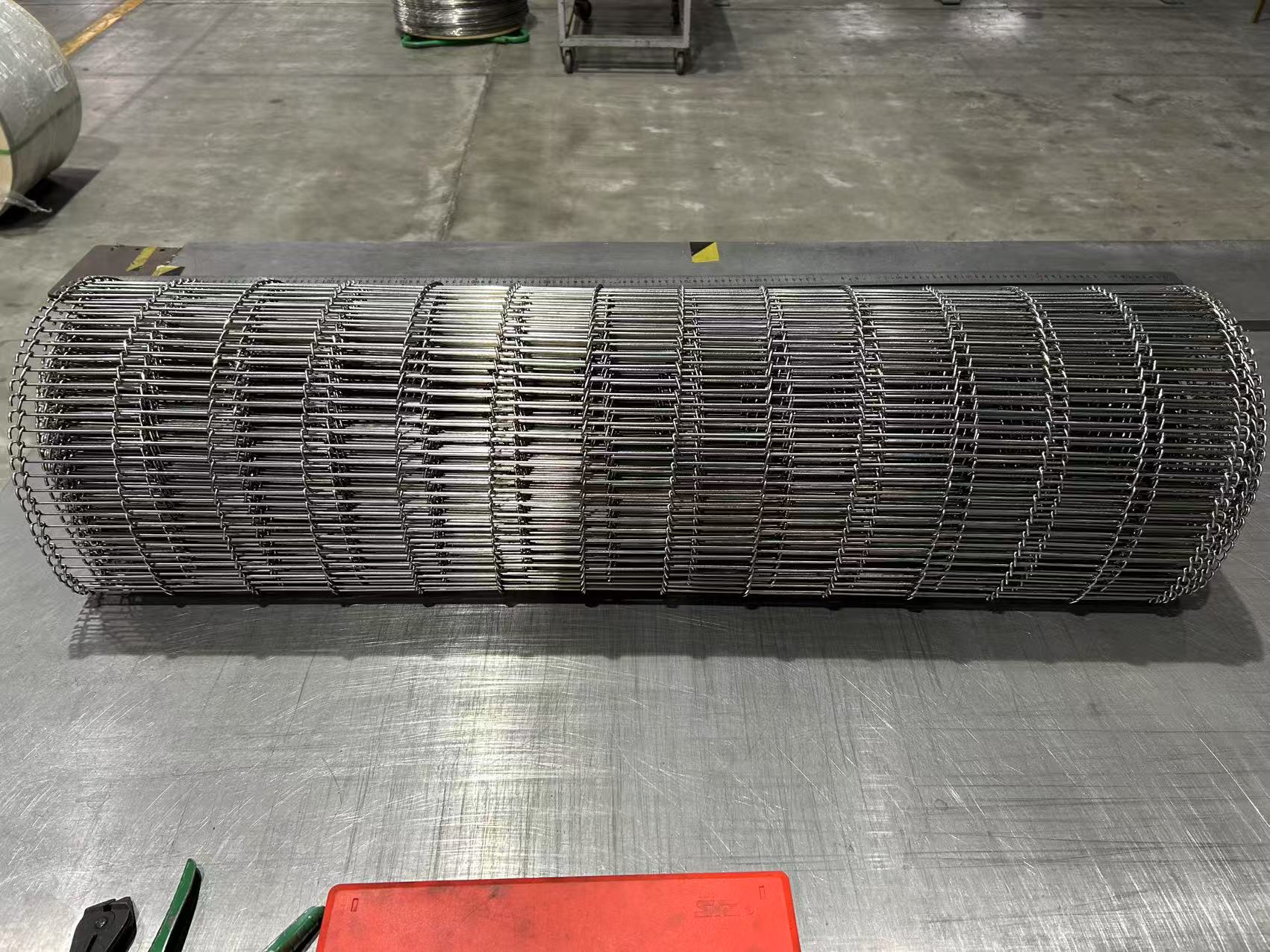
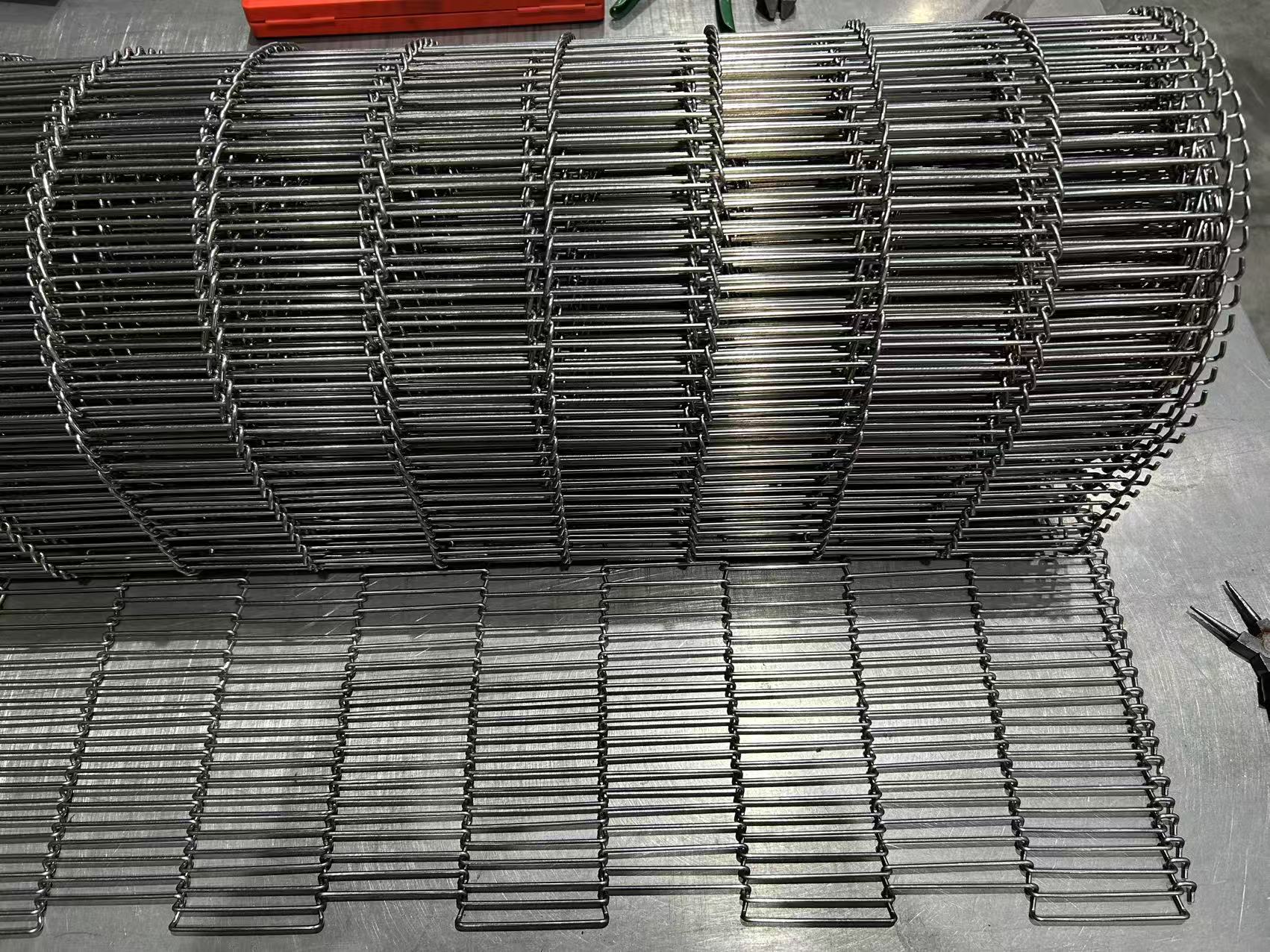
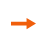
Ladder belt, a specialized type of metal conveyor belt, is named for its distinct ladder-like structure. It consists of parallel longitudinal side strips (typically made of metal sheets or profiles) connected by evenly spaced transverse cross rods, forming an open, rigid framework that balances load-bearing capacity and operational efficiency.
Component Composition: It comprises two key parts: longitudinal side strips (providing structural support and edge stability) and transverse cross rods (distributing loads evenly and enabling material conveyance).
Material Selection: Primarily manufactured from metals such as carbon steel (for general industrial use) and stainless steel (e.g., 304, 316L, suitable for corrosion-resistant or food-grade applications). High-temperature alloys (e.g., Inconel) are also used for extreme heat environments (up to 1000°C+).
Open Structure: The gap between cross rods creates an open mesh, facilitating airflow, drainage, and debris discharge—critical for processes requiring heat transfer, cleaning, or moisture control.
High Load-Bearing Capacity: The rigid connection between side strips and cross rods allows it to handle heavy or bulky materials (e.g., ores, castings) without deformation.
Dimensional Stability: Metal materials resist stretching, shrinking, or warping under temperature fluctuations or mechanical stress, ensuring consistent conveyor alignment.
Easy Maintenance: The simple ladder structure minimizes debris accumulation; damaged cross rods or side strips can be replaced individually, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
Food Processing: Stainless steel ladder belts are used for baking, frying,freezing, or washing lines (compliant with FDA/USDA standards, easy to sanitize).
Mining & Aggregates: Conveys coal, gravel, or minerals, leveraging high impact resistance and load capacity.
Heat Treatment: Transports workpieces through furnaces or cooling zones, with open structure enabling uniform heat penetration.
Recycling & Waste Management: Handles bulky recyclables (e.g., plastic, paper) while allowing small debris to fall through, optimizing sorting efficiency.




 Category:Ladder belt
Category:Ladder belt Material:
Material: Application:
Application: Visits:58103
Visits:58103 Email:
Email:
 Knowledge
Knowledge